I've written a free software program called
Multi-Sub Optimizer (MSO) to help with this problem. To use it, you make individual measurements of main speakers and each sub at each listening position you wish to optimize. Measurements must be made using REW's acoustic timing reference feature to ensure time-synchronized measurements. Then you export each measurement to a text file using
File, Export, Measurement as Text in REW. You import these files into MSO, and define your filter channels and associate these channels with the corresponding measurements you imported. You specify what kind of filters to use in each channel, and which measurements to sum together for each listening position. Then you run the optimization. Here is a "before and after" example with four subs and four listening positions.
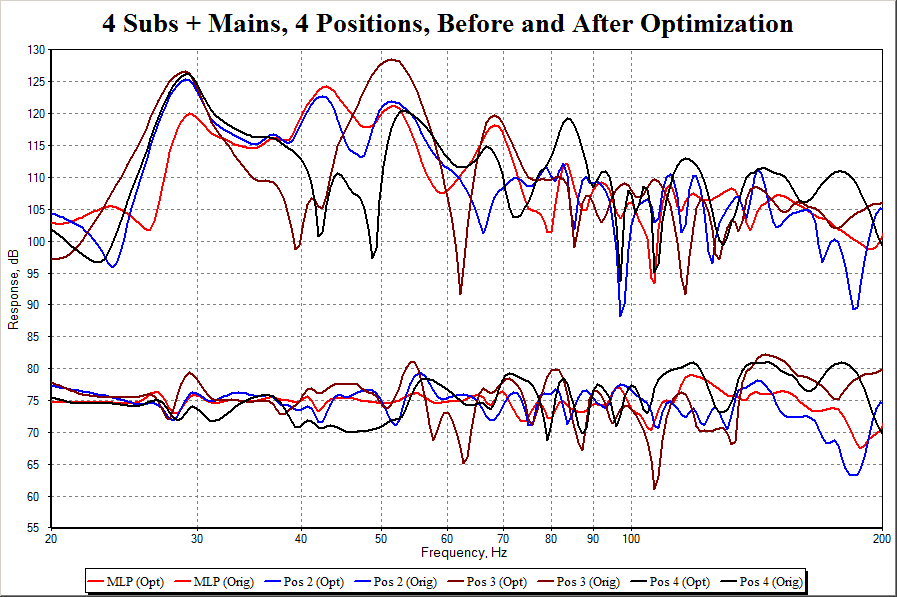
In this project, there were four subs, one pair of main speakers driven in mono, and four listening positions. So there were five measurements for each listening position, times four positions, for a total of 20 measurements. The optimization was run for about a half hour. If there were e.g. 1 million iterations of the optimizer, this would be the equivalent of trying out 1 million combinations of filter, delay and gain parameters and doing a measurement of the combined mains and subs for each of four listening positions, for a total of 4 million equivalent measurements. It's a lot easier to let the software do the work. You can see the optimization "runs out of gas" above about 100 Hz, because EQ is only applied to the subs, not the main speakers (although you can if you wish, and if your hardware supports it). Also, all PEQ filters used were cut-only, no boost.
For a manual procedure, you might check out
this thread.